Average Out of Pocket Tuition Payment Per Family After Loans Grants
How Do People Pay for College?
Report Highlights. Students apply financial assistance to pay for 92% of college didactics costs.
- Scholarships and grants cover $seven,500 of annual bookish costs per student.
- $120 billion in federal pupil aid goes out each twelvemonth in the class of grants, work-study, and loans.
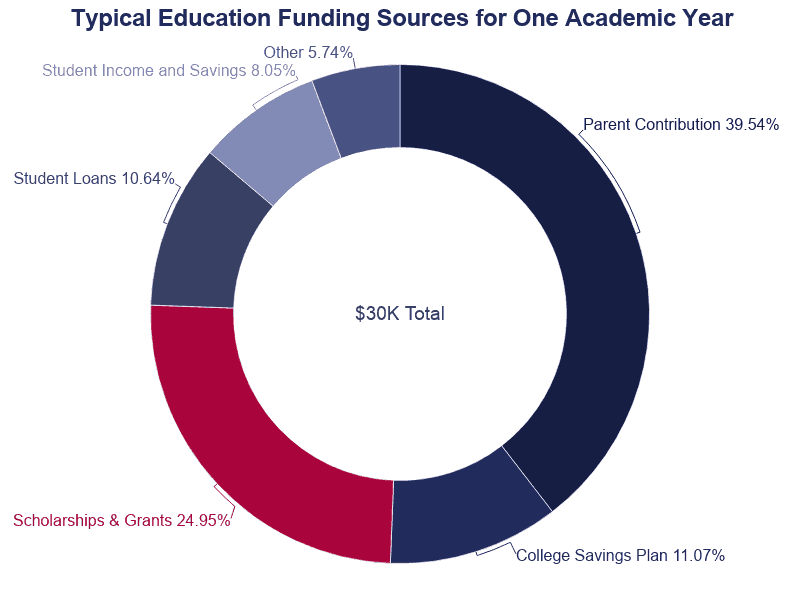
- Annually, parental contribution at $11,862 makes upward the largest share of a pupil's funding sources.
- 71% of college-bound students seek federal assistance to pay for college.
Related research includes Average Cost of College | Student Loan Debt Statistics | Student Loan Forgiveness Statistics | Average Cost of Community College | Average Time to Repay Pupil Loans | Economic Effects of Student Loan Debt | Educatee Loan Refinancing
How to Pay for College
College financial aid offices help students determine how they volition pay for school. Considering schools expect students to need financial aid to pay for higher, well-nigh schools offer complimentary financial counseling services for electric current and prospective students.
- 84% of students receive some grade of fiscal aid.
- Scholarships and grants cover $7,500 of annual academic costs per student.
- For federal and country government aid, the average accolade per student is $13,100.
- Students who nourish nonprofit private schools receive the most federal and state government aid.
- Parental support accounts for the greatest financial contribution to almost students' educations.
- Parental income and savings, parental borrowing, and college savings accounts embrace over half of students' educational expenses.
- Excluding higher savings plans, $11,900 is roughly how much parents pay for one academic year of their children's didactics.
- Long-term, high-yield savings accounts and holding mortgages are mutual strategies parents apply to pay for college educational activity.
Grants and Scholarships
Grants and scholarships offer free money to pay for college. Innumerable entities offering grants and/or scholarships, including federal and state governments, schools, customs organizations, private organizations, businesses, and nonprofits. Some institutions are founded for the sole purpose of providing one or more scholarships.
- Grants from the Part of Federal Student Aid (OFSA) at the U.Due south. Department of Educational activity (ED) are mostly need-based.
- Scholarships are available from other federal institutions, such as those within the Section of Health and Human Services (DHHS) and the U.S. Department of Labor.
- Current and would-exist students use for federal grants using the FAFSA.
- Federal grants are awarded on a year-to-year footing, so filing the FAFSA is an annual requirement to receive this type of student aid.
- Federal grants also require receiving students to maintain eligibility.
- Students who neglect to maintain eligibility may be required to pay back the grant coin in full or in office.
- Federal grants include the Federal Pell Grant, the Federal Supplemental Educational Opportunity Grant (FSEOG), the Teacher Education Assistance for Higher and Higher Education (TEACH) Grant, and the Republic of iraq and Transitional islamic state of afghanistan Service Grant.
- Pell Grants offering the maximum possible payment at $half-dozen,345 per bookish twelvemonth.
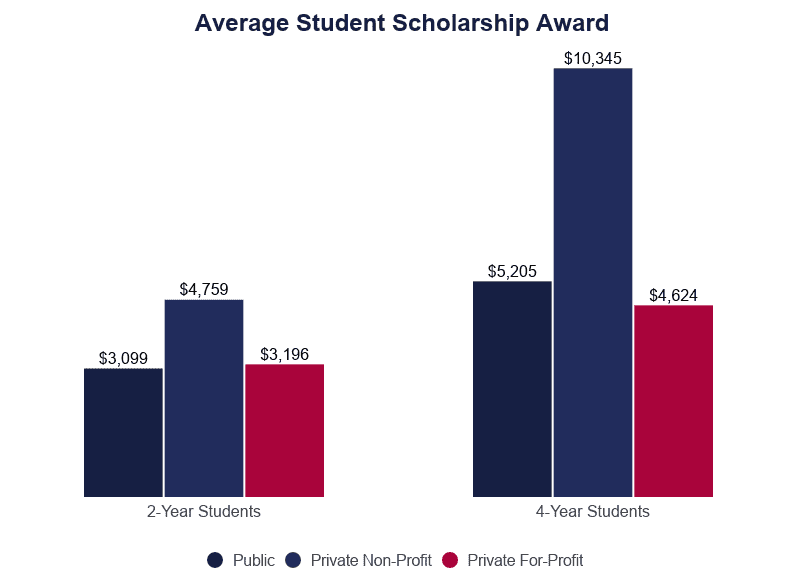
- Private non-profit schools also offer the most in institutional grants and scholarships.
- Many pocket-size, specialty grants are available to students, such textbook grants of $500-$1,000 per year.
Grant and Scholarship Statistics
Experts advise students to prioritize grant and scholarship applications using information and requirements. This helps students counterbalance their odds of success. Smaller scholarships for $500 or $one,000 offer much less competition than larger awards.
- 5 million scholarships make $24 billion bachelor to college students every twelvemonth.
- Scholarships and grants cover 25% of educational costs every twelvemonth.
- There is plenty public and individual scholarship money bachelor to give every full-time enrolled student $9,744.
- 63% of all undergraduates receive at least one grant or scholarship.
- 76.vii% of total-time undergraduates receive a grant or scholarship.
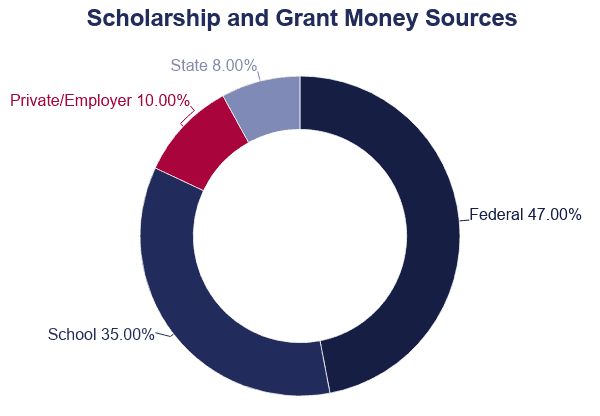
- 47% of all grants and scholarships come from the federal regime.
- 87% of students who receive scholarships receive ane from their college.
- 75% of students who are awarded scholarships receive them from individual or customs organizations.
- twenty one thousand thousand FAFSAs are candy each year.
- 23% of federal grants are Pell Grants.
- By not filing their FAFSA, students miss out on well-nigh $three billion in Pell Grants each year.
- 52% of high school graduates are eligible for a Pell Grant.
- 85% of first-fourth dimension, full-time students attending 4-year colleges receive federal assistance.
- 78% of first-time students at 2-yr colleges receive aid.
- 31% of college students come up from depression- to very low-income households.
- States provide more grants and scholarships based on test scores and grade point boilerplate (GPA).
- Most individual scholarships are less than $four,000.
- The odds of winning a private scholarship are about 1-in-8.
- For some very competitive scholarships, odds are as low as 1-in-500.
College Savings
High-yield savings accounts are popular for long-term savings with no withdrawals. Programs through the IRS also offer savings programs that include taxation benefits. It's mutual for parents to take advantage of these long-term savings plans on behalf of their children or grandchildren.
- Income and savings comprehend a majority of academic costs.
- 529 Plans, also known every bit Qualified Tuition Plans (QTPs) are state-sponsored education savings plans.
- 529s are substantially prepaid tuition plans, assuasive the purchase of college credits for future apply – simply at current prices – at a participating institution.
- Every land's 529 is available to the public, regardless of residency.
- Only certain institutions are canonical.
- 529s include tax benefits every bit authorized by the Internal Acquirement Service (IRS)
- Coverdell Education Savings Accounts are available just to those saving on behalf of a beneficiary who is either nether the historic period of eighteen or designated special needs.
- A Coverdell Educational activity Savings Account allows investors to put aside upwardly to $two,000 each year.
Higher Savings Statistics
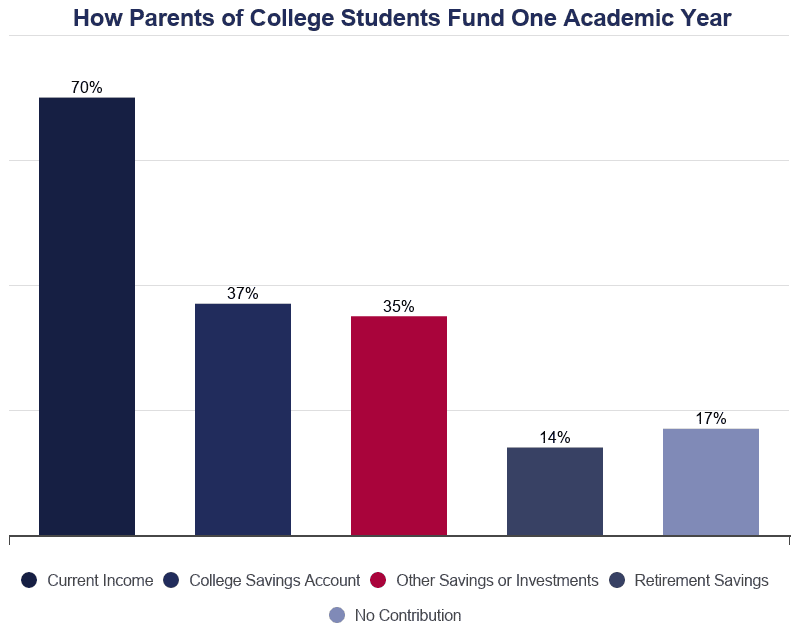
In almost families that include a college student, parent income and savings make up the bulk of instruction funding. This is non the example, however, in families where the student is the head of the household or in cases where the educatee is the master decision-maker in funding their educational activity.
- Student income and savings cover eight% of teaching costs.
- Student contributions, including funds borrowed and grants awarded, encompass 21% of education costs.
- 54% of students who are the head of their household report borrowing money to pay for school.
- Amidst students who are the primary fiscal conclusion-makers, $27,041 is the average amount they pay to attend higher for one academic yr.
- When parents are the primary decision-makers, they pay $34,461 for i academic twelvemonth.
- Parental income and savings embrace 44% of higher education costs.
- 83% of parents with children attending school pay for a portion of their child'due south education costs.
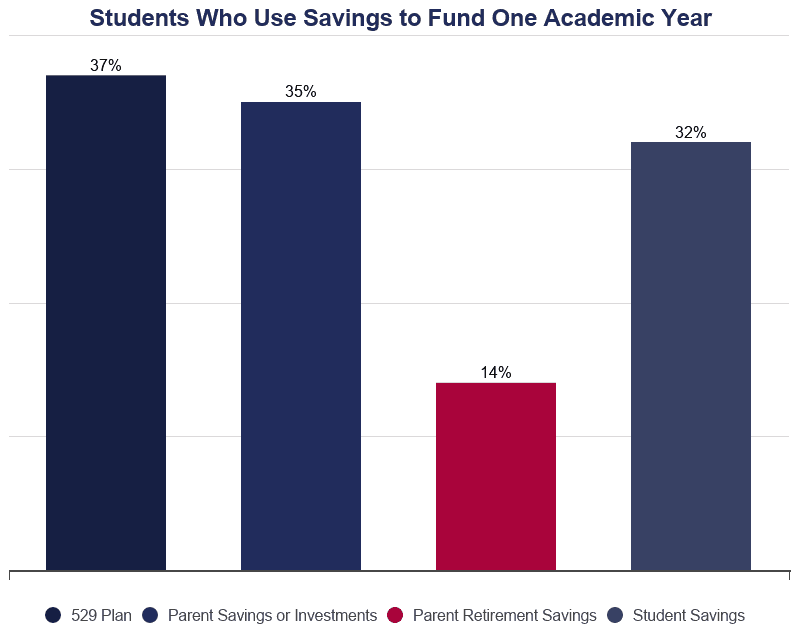
- 37% of them withdraw funds from a savings business relationship dedicated to college expenses.
- 14% of parents withdraw funds from a retirement account.
- 35% utilize other savings or investments to fund their child'south college education.
- 0.8% is an average almanac percentage yield (APY) for a high-yield savings business relationship.
- 1.25% is a high-end APY for a high-yield savings account.
- A savings account with an APY of i.25% and a $200 monthly contribution for 10 years volition have an stop balance of $25,622.45.
- Later on an additional ten years, the same account will contain $54,407.56.
Student Loans
About 45 1000000 American adults owe $i.7 trillion in student loan payments. Most student loans come from the federal government. Many private and fiscal organizations offering student loans, as well.
- Educatee loans by and large brainstorm accruing interest immediately; merely subsidized federal loans carry no interest until a student is out of school.
- Federal pupil assistance may exist used to pay for tuition, fees, books and supplies, room and board, transportation, and daycare for dependents.
- Students utilize for federal loans by filling out the Complimentary Awarding for Federal Student Aid (FAFSA).
- Undergraduate students tin borrow as much as $31,000 with a Federal Direct Loan.
- Private companies may offer loans up to 100% of the pupil borrower'south cost of attendance.
- Most private loans begin accruing involvement immediately, though payments may or may non be due until the educatee leaves school.
- Private companies are likely to accuse fees for late or incomplete payments.
- Individual companies are also more likely to offer discounts, such as reduced interest rates with automated payments.
- Some individual lenders deal exclusively in student loans.
Pupil Loan Statistics
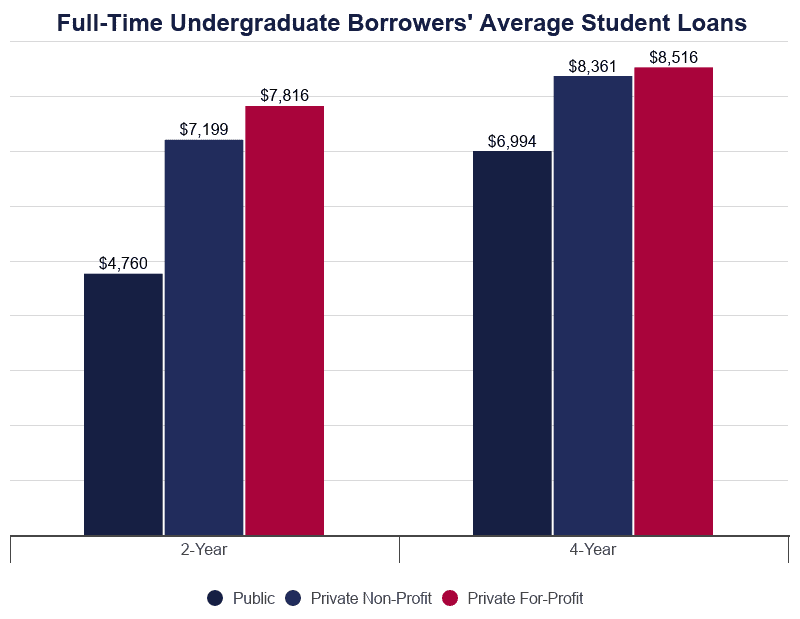
Almost students borrow money to pay for college at some bespeak during their didactics. Post-secondary students, including those earning certificates and associate'southward degrees, infringe at least $15,000 to pay for classes.
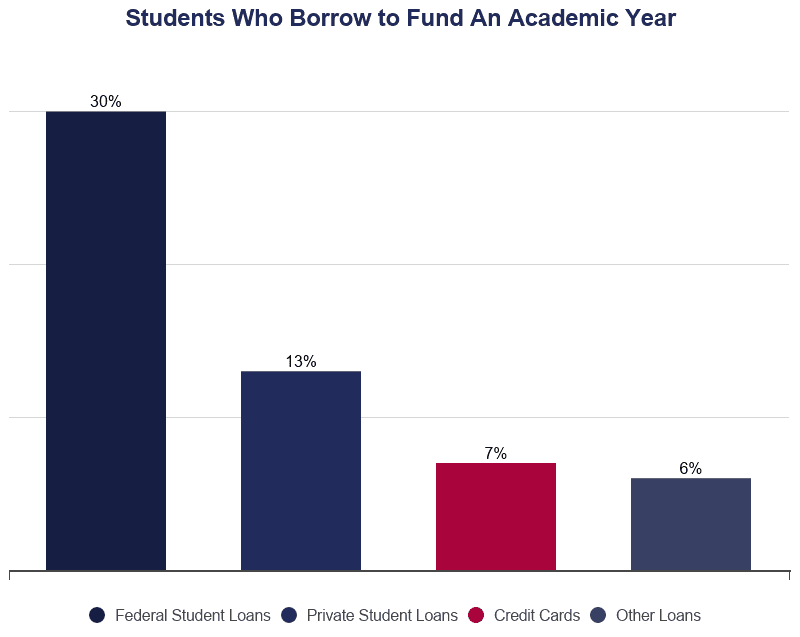
- 40.5% of undergraduates between the ages of xv and 23 use loans to pay for college.
- 53% of all students between the ages of 15 and 23 utilise educatee loans.
- Pupil loans comprehend 21% of almanac pedagogy costs.
- 34% of students infringe money to pay for college each twelvemonth.
- 20% of parents borrow money to pay for a kid'southward education.
- 71% of families use for federal student help by submitting their FAFSA.
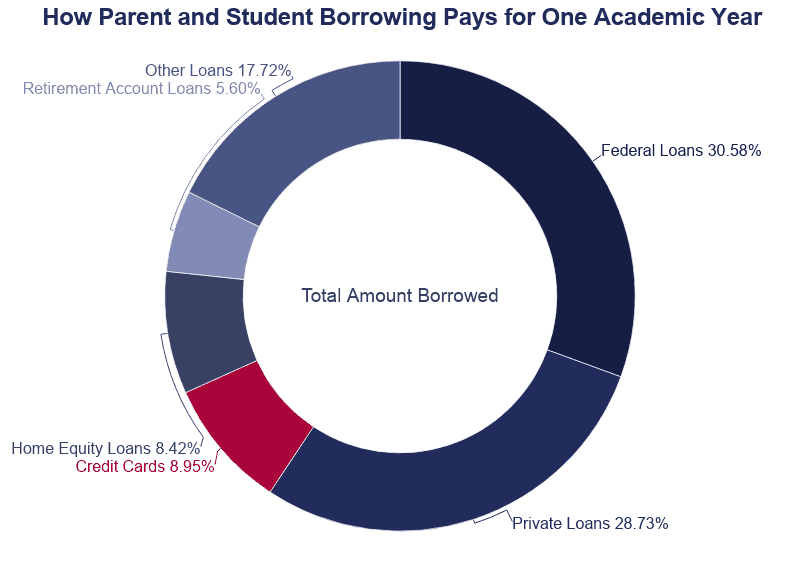
- 7.vii% of loans come up from private sources.
- The average college pupil borrows more than than $30,000 to attend school.
Loan Forgiveness Programs
How students pay for higher is a growing concern among teaching policymakers. As a result, the federal government has launched several student loan forgiveness programs. Loan forgiveness is also known as loan cancelation or loan discharge. It is tough to achieve, only not impossible.
- Most people may get eligible for loan forgiveness through the Public Service Loan Forgiveness (PSLF) Teacher Loan Forgiveness programs.
- Teacher Loan Forgiveness covers upward to $17,500 in outstanding loans.
- To accept their loans forgiven, most borrowers have to make several years of qualifying payments.
- Federal income-based repayment plans may make a borrower eligible for loan forgiveness later twenty-to-25 years of regular payments.
- Borrower defense belch eliminates part or all loan debt for students who attended schools that engaged in misconduct.
Loan Forgiveness Program Statistics
Every year, thousands of indebted borrowers become eligible for loan forgiveness just never apply. Some applicants submit a request for loan forgiveness multiple times before it is finally accustomed. Additionally, acceptance rates vary by program.
- Over 3 meg student loan borrowers are eligible or nearly eligible for student loan forgiveness.
- Only 6.7% of graduates eligible for loan forgiveness really apply.
- 11% of applicants benefit from full or fractional loan forgiveness.
- Some loan forgiveness programs have an acceptance charge per unit of less than 1%.
- At one point, the PSLF program accepted 0.03% of applicants.
- In recent months, nevertheless, PSLF has decreased its rejection rate by 250%.
Work-Study
Piece of work-written report programs aid students find role-time jobs that accommodate their academic requirements. These jobs usually include positions within the school, though jobs may exist off-campus likewise. Off-campus jobs are probable with local non-profit groups.
- The ED's Federal Work-Report Program prioritizes fiscal need, civics, and finding students work related to their field of report.
- Qualifying and applying for piece of work-study doesn't guarantee employment.
- Federal piece of work-report is available to total-time undergraduates, graduate, and professional person students.
- The federal program limits the number of hours a educatee may work.
- Most students are authorized to work between x and 20 hours per week.
- Off-campus jobs are unremarkably at non-profits, public institutions, or customs groups.
- Some schools have their own work-study programs independent of the ED.
- These programs may have their ain requirements, such as limitations on educatee eligibility.
- Schools may accept contracts with private companies to provide student employees.
- Work-report income does non apply on the FAFSA.
- Work-study students earn an average of $one,847 per academic year.
- 18% of all students participate in Federal work-study.
- 5% of undergraduates participate in piece of work-report.
- x.v% of full-time undergraduates participate in work-written report.
- 43% of full-time students are employed while in schoolhouse.
- Amongst those students, 23% work more than than 35 hours per week.
- 81% of part-time students are employed while taking classes.
- 58% of those students work more than 35 hours per week.
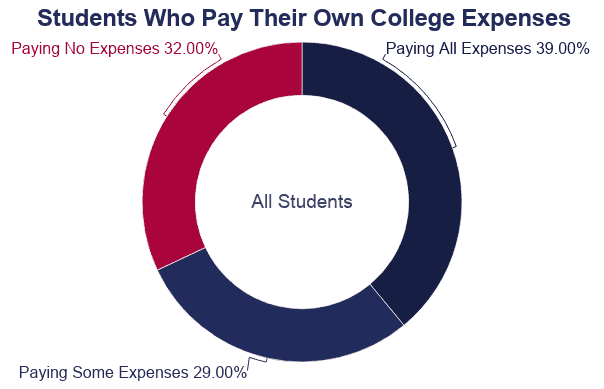
Aid for Military Families
Many types of student aid are available to armed services personnel, veterans, and their families. There are likewise reserve training programs and scholarships available through most branches of the military.
- Over ane,000 colleges participate in Reserve Officers' Training Corps (ROTC) programs.
- Army, Air Force, Navy, and Marine ROTC programs all offer scholarships.
- The Department of Veterans Affairs' GI Neb offers instruction benefits for vets, their dependents, and widows.
- Children of Iraq and Afghanistan service vets who died in combat after September xi, 2001 qualify for multiple boosted education benefits.
- Low-involvement and no-interest educational loans are also bachelor to armed forces personnel and their families.
Education Taxation Benefits
The IRS offers student expense relief in the form of tax credits. If a pupil is required to pay taxes, they may reduce the amount of their taxable income using these credits. The IRS also offers deductions on educatee loan involvement and special savings accounts for educational expenses.
- The American Opportunity tax credit allows a deduction of up to $2,500 per student, per year for the outset four years the educatee is in school.
- The Lifetime Learning credit allows a claim of up to $2,000 per student, per year on expenses required for college- or career school-related course piece of work.
- Student loan involvement may qualify students or their families an annual deduction of up to $ii,500.
- Coverdell contributions are not taxation deductible, only any growth is tax free until its withdrawn.
- Qualified tuition programs, also known as QTP and 529 plans, offering savings accounts that permit tax-free withdrawals.
- The IRS tin can also accommodate penalization-free early on withdrawals from an individual retirement account (IRA) for college costs.
Aid for Foster Care Youth
Children in foster care age out of the system on their 18th birthday. While many students receive financial aid from family into legal adulthood. To aid students who are unlikely to receive aid from parents or relatives, public and individual programs offset the financial brunt of higher instruction.
- Educational and Grooming Vouchers (ETV) for electric current and former foster care youth are available through the John H. Chafee Foster Intendance Independence Program.
- Students may receive up to $5,000 each year they are in schoolhouse through the plan.
- Aid is available to old foster youth upward to the age of 21.
- States have varied processes for ETV program application submissions.
- The Foster Intendance Managing director at whatsoever country Child Welfare Agency has more than data about how to apply for an ETV.
- Some states also offer tuition waivers.
- Additional programs are available through DHHS.
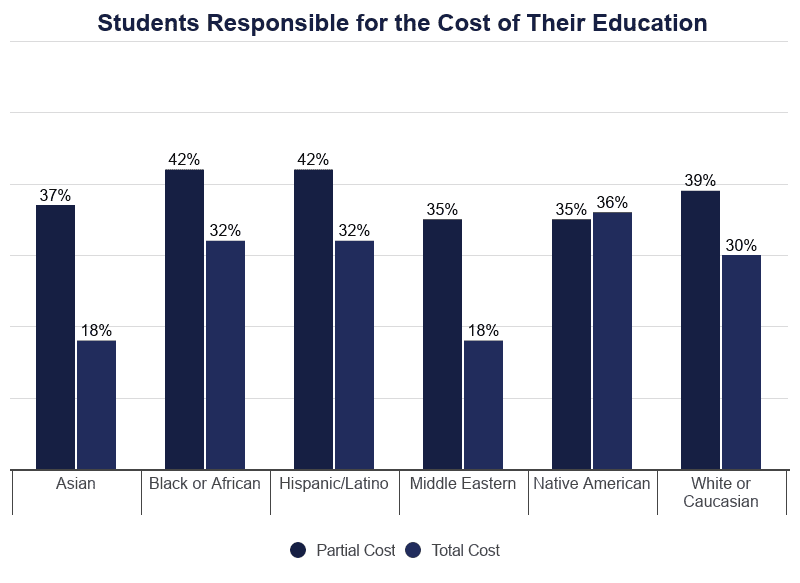
Higher Funding Demographics
Education funding sources vary from one private to the next. Organizing people into categories uncovers patterns that indicate what factors may affect the affordability of a college education.
- 36% of Native American students are responsible for financing the total price of their college education.
- Midwestern students are the least likely to receive whatever exterior help paying for college.
- 35% of Midwestern students are responsible for the entire price of their education.
- 51% of international students are non responsible for financing their higher education.
- 57% of students majoring in public policy are responsible for the total cost of their education.
- 55% of classics majors are not responsible for financing any of their education.
Sources
- United States Department of Education (ED) Function of Federal Student Aid (OFSA), Data Center
- National Center for Education Statistics (NCES), Digest of Education Statistics
- U.S. News, 12 Ways to Cut Your Textbook Costs
- U.S. News, Do Students Have to Pay Back Financial Help?
- U.Southward. News, Best Individual Educatee Loans of 2020
- Stanford Academy, 8 Things You lot Should Know Most Federal Work-Report
- NCES, The Condition of Education
- Sallie Mae, How America Pays for Higher 2020
- Internal Revenue Service (IRS), Publication 970 (2019), Revenue enhancement Benefits for Education
- CNN, How The Average Family Pays for College
- LendEdu, Who is Paying for College? It Might Depend on Race or Institution
- U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission, An Introduction to 529 Plans
Source: https://educationdata.org/how-do-people-pay-for-college
0 Response to "Average Out of Pocket Tuition Payment Per Family After Loans Grants"
Post a Comment